Indiana regulators approve settlement cutting I&M electric rates
State regulators have approved a settlement with Indiana Michigan Power under which the utility will cut its Indiana residential customers’ base electric rates nearly 6% by next year.
State regulators have approved a settlement with Indiana Michigan Power under which the utility will cut its Indiana residential customers’ base electric rates nearly 6% by next year.
The Indiana General Assembly has overwhelmingly passed a bill that would allow electric utilities to build small modular reactors, a move that could pave the way for commercial nuclear power in the state for the first time.
The 1-gigawatt power plant in southwestern Indiana is currently owned by Hoosier Energy and is approaching retirement.
More than 3.5 million acres of southern Indiana—from just south of Indianapolis to near Jasper and from the Illinois border to near Madison—is now designated as the Southern Indiana Sentinel Landscape.
Long-delayed cleanup of Great Lakes harbors and tributary rivers fouled with industrial toxins will accelerate dramatically with the $1 billion boost, senior administration officials say.
The early deliberations come days after a group of vulnerable Senate Democrats introduced a bill that would suspend the gas tax of roughly 18 cents per gallon for the rest of the year.
The agreement comes more than two years after a discharge of ammonia and toxic chemicals killed thousands of fish and closed Lake Michigan beaches, the federal government said Monday.
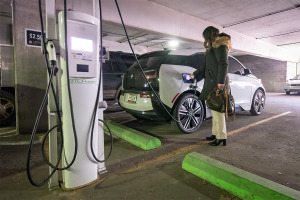
House Bill 1221 outlines parameters for utility regulators to use when considering utilities’ proposals for constructing charging stations and setting consumer rates for their use.
Novus Capital Corp. II announced in September it would merge with Energy Vault in a deal that would take the 4-year-old company public. The transaction gives Energy Vault an immediate cash infusion of $355 million.

The Eagle Valley power plant in Martinsville is one of three generating stations that provides electricity for about 500,000 AES Indiana customers in central Indiana.
IBJ reporter John Russell joins the podcast to talk about why the Indiana Legislature is consider a proposal that could help clear a path for smaller, modular nuclear reactors to be located in Indiana.

Some once-leery states, including Indiana, are taking a new look at nuclear power as a way to preserve jobs and help decarbonize the electric grid.
The White House is aiming to shift the nation’s electricity supply to cleaner energy in the face of congressional resistance and a Supreme Court that could limit the federal government’s ability to tighten public health standards.
Progress Rail, a subsidiary of Caterpillar Inc., says the locomotives use no fuel and emit zero exhaust emissions.
The parent company of utility AES Indiana has parted ways with its top U.S. utility executive in what the company is calling a mutual separation.
Indiana lawmakers are taking another stab at setting up statewide standards for large wind and solar projects, a year after a group of counties shot down an earlier effort.
The vote represents a major shift for Indiana, which has never had commercial nuclear power and has long relied on coal to power homes and factories.
As climate change pushes states in the U.S. to dramatically cut their use of fossil fuels, many are coming to the conclusion that solar, wind and other renewable power sources might not be enough to keep the lights on.
Fishers-based American Resources Corp. said the effort will put the partners on the path to becoming the first and lowest-cost producer of domestically-sourced, purified and sustainable battery and magnet metals.
Plants in four states, including Indiana, will have to close the coal ash ponds months or years ahead of schedule, the EPA said Tuesday, citing deficiencies with groundwater monitoring, cleanup or other problems.